Redis Clusters
Recently I have been spending some time figuring out various clustering techniques that can be used in setting up redis cluster environment in cloud (AWS) or otherwise. First, AWS has elasticache which has redis option but elasticache doesn’t support cross-region replication and in doesn’t allow more than 5 read replicas (maybe it will in future releases of elasticache) - which was not meeting our requirements so we decided to stand our own redis cluster on ec2 intances. This gave us more flexibilty but yes - we have to take care of monitoring and some setups ourself which otherwise could have been taken care by elasticache. But thats Ok because redis configurations are not very complicated and for monitoring, We were planning to use influxdb/telegraf combination and not cloudwatch.
Anyhow, I did couple of POCs around pure redis-sentinel cluster and realized that we need some proxies like HAProxy, TWEM Proxy (nutcracker), OneCache etc to make maximum preformance, resilience and availabilty.
Few important things to note down in redis:
- No master-master replication.
- A slave can’t have multiple masters.
- One redis cluster can’t have more than one master [twemproxy supports multi-masters but technically creates different clusters for each shard].
Redis-Sentinel
Sentinel provides HA to redis cluster without human intervention. Sentinel cluster monitors the master and in case master node goes down, Sentinel does polling among themselves to choose a slave to be promoted as new master. There are different configuration and setup and you can read more about those at redis’s portal.
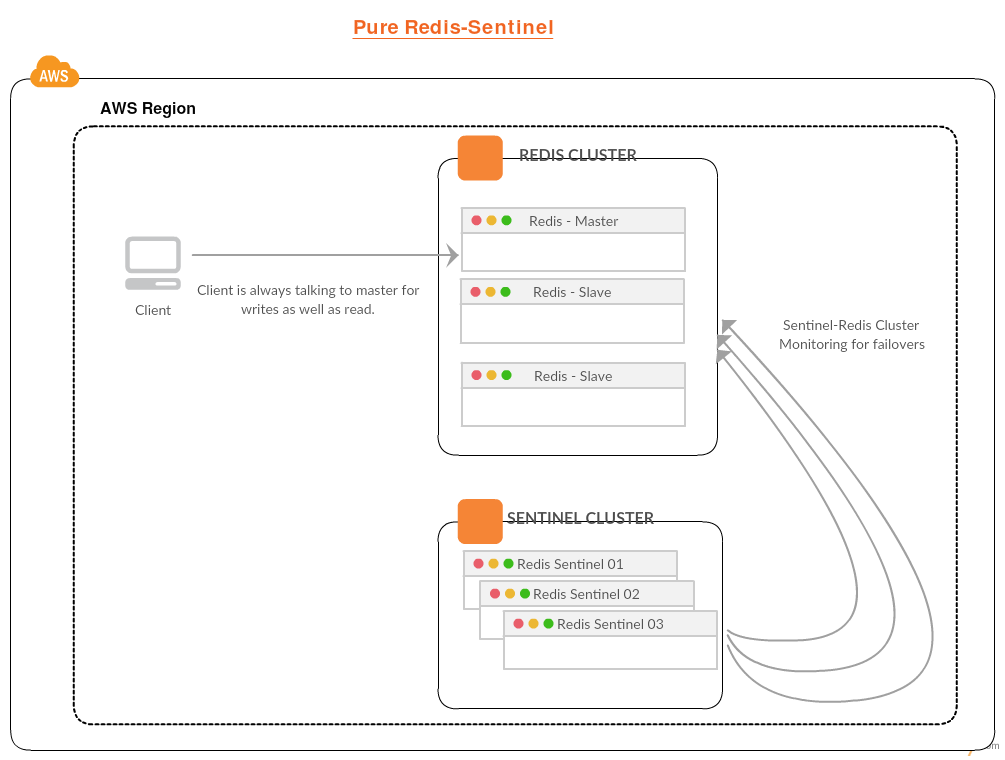
In this setup, There is no external proxy or process which can distinguish between master/slave nodes. So the client is directly connecting to the master at all times for write/read operations. The disadvange of this setup is there is:
- client is connecting to single node for read/write operations which could be a performance bottleneck as slaves are sitting idle while they could have been very well used for read operations.
- This solution is not scalable because there is just one write/master in the infrasturcture.
- There is no external process/proxy to route read/write traffic.
- Clients needs to have the knowledge of sentinel clusters to get the current master node to connect to.
To overcome these challanges, We can use twem, haproxy, onecache etc. I did a comparision prototype on HAProxy & TWEM proxy (nutcracker). Here are my learnings
HAProxy:
HAProxy is a matured and time tested proxy for number of platforms including Redis cache. HAProxy also has a web interface to monitor frontend/backend traffic. In my setting, I created two HAProxies - One for write (which has master) and other one for read only. This allows to horizontally grow the cluster for reads and directing all write traffic to write cluster. The nodes on the read HAproxy cluster are basically slaves of the master node. When master goes down, the write proxy will automatically choose the new master (without the need of any external process though the new master is chosen using Redis’s sentinel process).
Proxy’s backend configuration for WRITE:
This will select only the node which is master to forward the traffic. “tcp-check expect string role:master” will make sure that this backend connects to the node which is currently a master.
frontend ft_redis
bind *:6378 name redis
default_backend bk_redis
backend bk_redis
balance first
option tcp-check
tcp-check connect
tcp-check send PING\r\n
tcp-check expect string +PONG
tcp-check send info\ replication\r\n
tcp-check expect string role:master
tcp-check send QUIT\r\n
tcp-check expect string +OK
server redis_6380 localhost:6380 check inter 1s
server redis_6381 localhost:6381 check inter 1s
server redis_6388 localhost:6388 check inter 1s
server redis_6389 localhost:6389 check inter 1s
Proxy’s backend configuration for READ ONLY:
frontend ft_redis
bind *:6379 name redis
default_backend bk_redis
backend bk_redis
option tcp-check
tcp-check connect
tcp-check send PING\r\n
tcp-check expect string +PONG
tcp-check send info\ replication\r\n
tcp-check expect string role:slave
tcp-check send QUIT\r\n
tcp-check expect string +OK
server redis_6388 localhost:6388 check inter 1s
server redis_6389 localhost:6389 check inter 1s
server redis_6380 localhost:6380 check inter 1s
server redis_6381 localhost:6381 check inter 1s
In write cluster, At any time, the traffic will be directed to any ONE of the node (master) while readonly cluster will have n-1 nodes listening at all times.
The advantage of using HAProxy is that we don’t need any external process to moitor the switching-over of master and re-configure the HAProxy’s settings to point to new master.
The limitations on the other hand is that if your requirement is of very high volume writes i.e. greater than 100K WPS then it is difficult to scale becasue we can’t have more than one write cluster. In those cases, You may have to consider using twem proxy by twitter.
Twem Proxy:
Twitter’s official version of twem proxy (nutcracker) doesn’t support Sentinel and also the community is not very active.
Sentinel not support by official twem
Though I found a forked repository of twem which works with Sentinel and the maintainers are very active.
Git link to TwemProxy with Sentinel You first need to create your multiple redis clusters with sentinel. In the nutcracker.yml, provide all the masters in each cluster at the start time. Twem will automatically update the yml file with any new master in event of switchover.
sigma:
listen: 127.0.0.1:22125
hash: fnv1a_64
distribution: ketama
auto_eject_hosts: false
redis: true
server_retry_timeout: 2000
server_failure_limit: 1
servers:
- 127.0.0.1:6379:1 redis-server-cluster1
- 127.0.0.1:6380:1 redis-server-cluster2
sentinels:
- 127.0.0.1:16379:1
- 127.0.0.1:16380:1
- 127.0.0.1:16381:1
Sentinel configuration:
# Host and port we will listen for requests on
bind 127.0.0.1
port 16380
#daemonize yes
#
# "redis-cluster" is the name of our cluster
#
# each sentinel process is paired with a redis-server process
#
sentinel monitor redis-server-cluster1 127.0.0.1 6380 2
sentinel down-after-milliseconds redis-server-cluster1 5000
sentinel failover-timeout redis-server-cluster1 10000
sentinel config-epoch redis-server-cluster1 57
sentinel leader-epoch redis-server-cluster1 80
sentinel known-slave redis-server-cluster1 127.0.0.1 6381
sentinel known-sentinel redis-server-cluster1 127.0.0.1 16382 af319b1ae87a7e4878bf29bc037f91886c5a0f00
sentinel known-sentinel redis-server-cluster1 127.0.0.1 16381 8dde7e4b7f7cc6492944085eab328f7dc1cbca60
sentinel known-sentinel redis-server-cluster1 127.0.0.1 16383 fa43cf765a33e678598581700c843d36fa6b4b8c
sentinel monitor redis-server-cluster2 127.0.0.1 6382 2
sentinel down-after-milliseconds redis-server-cluster2 5000
sentinel failover-timeout redis-server-cluster2 10000
# Generated by CONFIG REWRITE
dir "/Users/acv631/Documents/Learning/redis/for-twem/node1"
sentinel config-epoch redis-server-cluster2 82
sentinel leader-epoch redis-server-cluster2 82
sentinel known-slave redis-server-cluster2 127.0.0.1 6383
sentinel known-sentinel redis-server-cluster2 127.0.0.1 16382 af319b1ae87a7e4878bf29bc037f91886c5a0f00
sentinel known-sentinel redis-server-cluster2 127.0.0.1 16381 8dde7e4b7f7cc6492944085eab328f7dc1cbca60
sentinel known-sentinel redis-server-cluster2 127.0.0.1 16383 fa43cf765a33e678598581700c843d36fa6b4b8c
sentinel current-epoch 82
The advantage of TwemProxy is that it shards the data into different Redis clusters based on your data key. This allows a very nice horizontal scaling. and if we are using sentinel then we will have the benefit of full HA as well.
If you dont want to use the forked version of twem that I have mentioned above, you can use the official one and there are plugins/agents available that can monitor sentinel for switchover events and re-configure twem’s configuration file at runtime. One of such agent is this.
To achive maximum results and scalabilty, We can use the HAProxy and TwemProxy combination which can give us the HaProxy’s abilty to isolate read/write traffic and Twem’s ability to shard. Please see this setup which is using both the proxies but it all depend on your individual usecase.
Elasticache
If you are OK with maintaining 2 URLs for Read and Write, you can also think about using elasticache by AWS which has one primary write cluster and upto 5 secondary read replicas. The write cluster’s public endpoint doesn’t change as it internally takes care of switching of master in case of failure. For read replicas, you can have them behind HAproxy or ELB.
